OVARIAN STIMULATION
Among the major Causes of Infertility in woman, 30% cases is due to an ovarian problem (absence of ovulation or rare and/or poor-quality ovulation). An Ovulation problem is any condition (usually hormonal) that prevents a mature egg from developing in your ovaries.
What is Ovarian Stimulation?
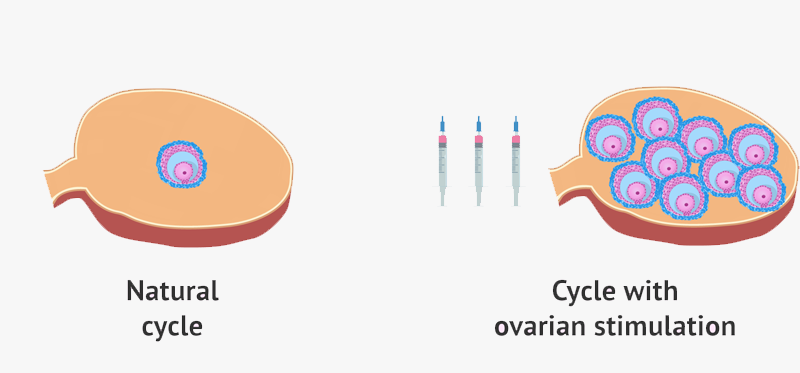
Ovarian stimulation involves the administration of hormones to a woman either orally or through injections so that the quantity and quality of mature follicles produced by the ovaries improves.
Some common medicines used to treat Ovulatory problem in women include:
- Clomiphene citrate (Clomid®) is a medicine that causes ovulation by acting on the pituitary gland. It is often used in women who have PCOS(Poly cystic Ovarian Syndrome) or other problems with ovulation. This medicine is taken orally.
- Human menopausal gonadotropin or hMG (Repronex®; Pergonal®) are medicines often used for women who don’t ovulate because of problems with their pituitary gland—hMG acts directly on the ovaries to stimulate ovulation. It is an injected medicine.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone or FSH (Gonal-F®; Follistim®) are medicines that work much like hMG. It causes the ovaries to begin the process of ovulation. These medicines are usually injected.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) analog are medicines often used for women who don’t ovulate regularly each month. Women who ovulate before the egg is ready can also use these medicines. Gn-RH analogs act on the pituitary gland to change when the body ovulates. These medicines are usually injected or given with a nasal spray.
- Metformin (Glucophage) is a medicine doctors use for women who have insulin resistance and/or PCOS. This drug helps lower the high levels of male hormones in women with these conditions. This helps the body to ovulate. Sometimes clomiphene citrate or FSH is combined with metformin. This medicine is usually taken by mouth.
- Bromocriptine (Parlodel®) is a medicine used for women with ovulation problems because of high levels of prolactin. Prolactin is a hormone that causes milk production.
When is Ovarian Stimulation Suggested?
During the initial workup of a Female Partner, if it is evident that there are issues with ovulation , Doctor usually suggests couple of cycles of Ovarian Stimulation
How is it done?
There are different levels of ovulation induction commonly used to treat infertility related to ovulation disorders, male factor or unknown causes. One method of treatment involves clomiphene citrate (Clomid or Serophene) taken in pill form for 5 days at the beginning of a cycle. For women whose only infertility problem is anovulation, up to 80% of patients will ovulate using this medication and 50% of those will conceive . Clomiphene may be combined with intrauterine insemination to boost the success of the medication by placing the sperm and egg in closer proximity to each other.
SuperOvulation
Superovulation might benefit if the patient has not responded to simpler ovulation inducing medications (such as clomiphene tablets).
Superovulation is a more aggressive level of ovulation induction. This treatment uses gonadotropins or sometimes a combination of clomiphene and gonadotropins to stimulate the production of multiple eggs. Patients undergoing superovulation must be closely monitored by blood tests and ultrasounds. Monitoring ensures that the patient does not hyperstimulate and also helps the physician administer the correct dosage of medication so that only a few follicles develop. This is a critical step to keeping the multiple pregnancy rates low. At the end of the superovulation treatment process, a low dose HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) may be prescribed to stimulate ovulation. Ovulation will occur between 24-36 hours after HCG. The patient is instructed to either have intercourse during this time or to come in for an Intrauterine Insemination. Depending on the cause of infertility, the success rate per superovulation treatment cycle is approximately 10-20% based on the woman’s age.
What should I expect during treatment?
Your treatment usually starts on day three or four of your menstrual cycle and lasts approximately eight to ten days. You will most likely have 5 to 6 clinic appointments for blood tests and/or vaginal ultrasounds to monitor your response and adjust your medication dose.
Your appointments will become more frequent toward the time of ovulation.
When the blood tests and ultrasounds indicate one to four mature follicles, one of our doctors will prescribe a second medication (hCG) to trigger ovulation. You will usually ovulate 36 to 48 hours after this final injection.
You will be asked to time your intercourse accordingly and if IUI has been planned by your doctor, you will be asked to visit the clinic approximately 24 to 36 hours after the hCG injection. This is accomplished by inserting a specially prepared sample of your partner’s semen through the cervix and placing it near the top of your uterus where it has the best chance of fertilizing an egg. The procedure takes only a few minutes and should be relatively painless.
Side Effects or Complications
There are risks associated with the use of ovulation induction medications including an increase in the chance for high order multiple births and the development of ovarian cysts. You may experience bloating, breast tenderness, cramping, pelvic twinges or heaviness, fatigue, and headaches.
A rare side effect that can occur is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS); symptoms include severe pain in the pelvis, abdomen and chest, nausea, vomiting, bloating, weight gain and difficulty breathing.
Please refer to our Treatment Service Quick Reference Chart to get more details about cost of treatment.
